2.2.4 Quaternion representation
Fixed angle representation and so far have drawbacks when interpolating intermediate orientations. A better approach is to use quaternions. A quaternion is a four-tuple of real numbers, [s,x,y,z], or [s,v] consisting of a scalar s, and a three-dimensional vector, v.
The quaternion contains the same information in a different form that can be interpolated as well as a single representation. The axis and angle information of quaternion can be viewed as an orientation of an object relative to its initial object space definition, or as the representation of a rotation to apply to an object definition. In the view of orientation, interpolating between represented orientations is important in generating key-frame animation. In the view of rotation, it is useful to apply a single, compound transformation to an object definition.
Basic Quaternion math
A bullet operator represents dot product, and "X" denotes cross-product. Quaternion addition is simply the four-tuple addition, [s1,v1]+[s2,v2]=[s1+s2,v1+v2]. Quaternion multiplication is defined as below, it is associative but not commutative.

A point in space or the vector from the origin to the point is represented as [0,v].

The inverse of a quaternion [s,v]^(-1) is obtained by negating its vector and dividng both parts by the magnitude squared.

Representing rotations using quaternions
A rotation is represented in a quaternion form by encoding axis-angle information. A Unit Quaternion represents a rotation of angle, theta, about a unit axis of rotation. (x,y,z).
QuaternionRot(theta,(x,y,z)) = [cos(theta/2), sin(theta/2)(x,y,z)]
Rotating some angle around an axis is the same as rotating the negative angle around negated axis. q=[s,v] is equivalent to -q =[-s,-v].

Rotating vectors using quaternions
A series of rotations can be concatenated into a single representation by quaternion multiplication.
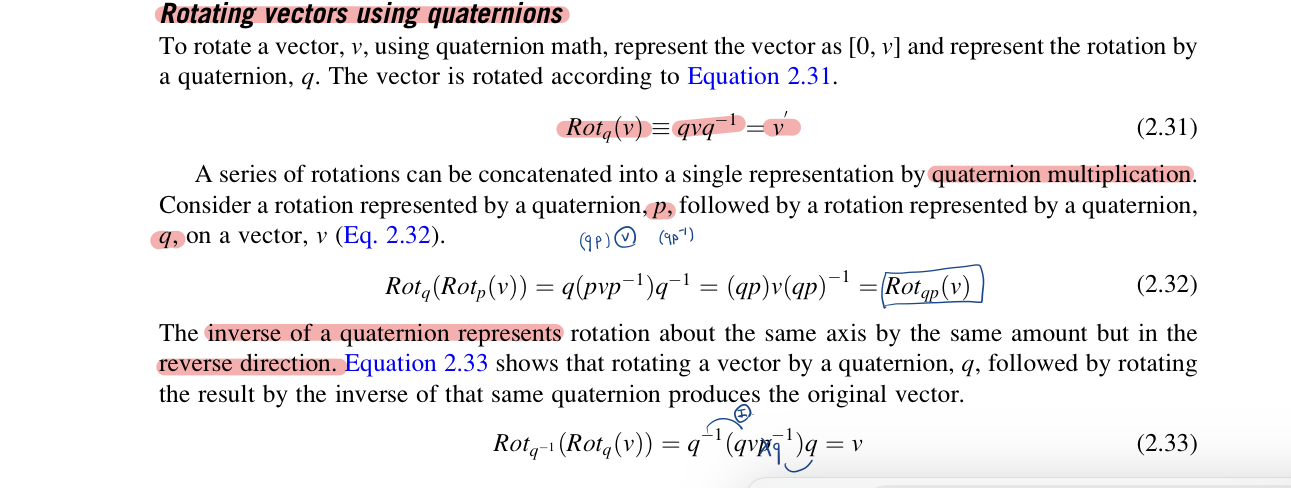
Inverse of a quaternion represents rotation about the same axis by the same amound but in the reverse direction. Also notice that in performing rotation, qvq^(-1), all effects of magnitude are divided due to the multiplication by the inverse of the quaternion. Thus scalar multiple represents same rotation as the unit quaternion.
Exponential map representation
Exponential map represents an orientation as an axis of rotation and an associated angle of rotation as a single vector. The direction of the vector is the axis of rotation and the magnitude is amount of rotation. Zero rotation is assigned to the zero, making the continuous representation. An exponential map uses three parameters which have well-formed derivatives. These are improtant for angular velocity.
Summary
The most robust representation of orientation is quaternions, but fixed angle, Euler angle, and axjis-angle are more intuitive. Fixed angle and euler angles suffer from gimbal lock and axis-angle is not easy to composite, but they are useful in some situations. Exponential map also do not concatenate well but offfer derivatives of orientation.
'ComputerGraphics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Controlling the motion of a point along the curve (0) | 2022.10.31 |
|---|---|
| Interpolating Values (0) | 2022.10.31 |
| Orientation representation (0) | 2022.10.26 |
| Error consideration (0) | 2022.10.24 |
| Homogeneous coordinates and the transformation matrix (0) | 2022.10.23 |




댓글